Introduction to Protective Clothing
Protective clothing is essential equipment for workers in various industries, including construction, healthcare, firefighting, chemical industries, mechanics, and heavy industries. The primary purpose of protective clothing is to shield the body from hazardous elements such as dust, chemicals, high temperatures, impacts, and environmental risks.
Protective clothing not only helps safeguard workers’ health but also enhances work efficiency. It is a crucial piece of equipment that reduces workplace accidents and ensures safety for employees.
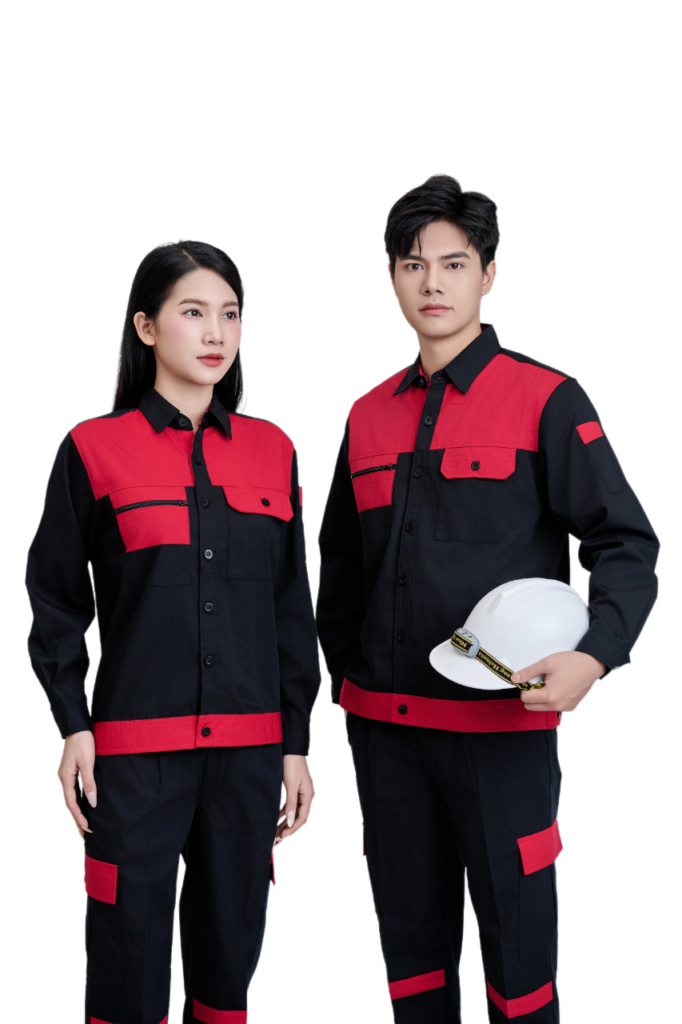

You may be interested in: FMF construction protective gear.
Importance of Protective Clothing
Equipping workers with protective clothings offers several benefits:
- Protects the body from hazardous elements: Such as dust, chemicals, bacteria, UV rays, high temperatures, and impact injuries.
- Reduces the risk of workplace accidents: Minimizes injuries caused by environmental hazards.
- Ensures workers’ health: Limits exposure to harmful substances, promoting long-term well-being.
- Enhances professionalism and uniformity: Reflects a company’s concern for its employees and fosters a professional work environment.
- Increases productivity: When workers are well-protected, they perform better and are less affected by hazardous work conditions.
Types of Protective Clothings
1. By Industry
- Labor protective clothing: Used in construction, mechanics, and electrical work.
- Medical protective clothing: Used in hospitals and laboratories to prevent exposure to bacteria and viruses.
- Chemical-resistant clothing: Waterproof and acid-resistant, designed for workers handling hazardous chemicals.
- Flame-resistant and heat-resistant clothing: Suitable for firefighting, metallurgy, and high-temperature environments.
- Radiation protection clothing: Used in nuclear power plants and radiation laboratories.
- Food industry protective clothing: Ensures hygiene and safety in food processing facilities.
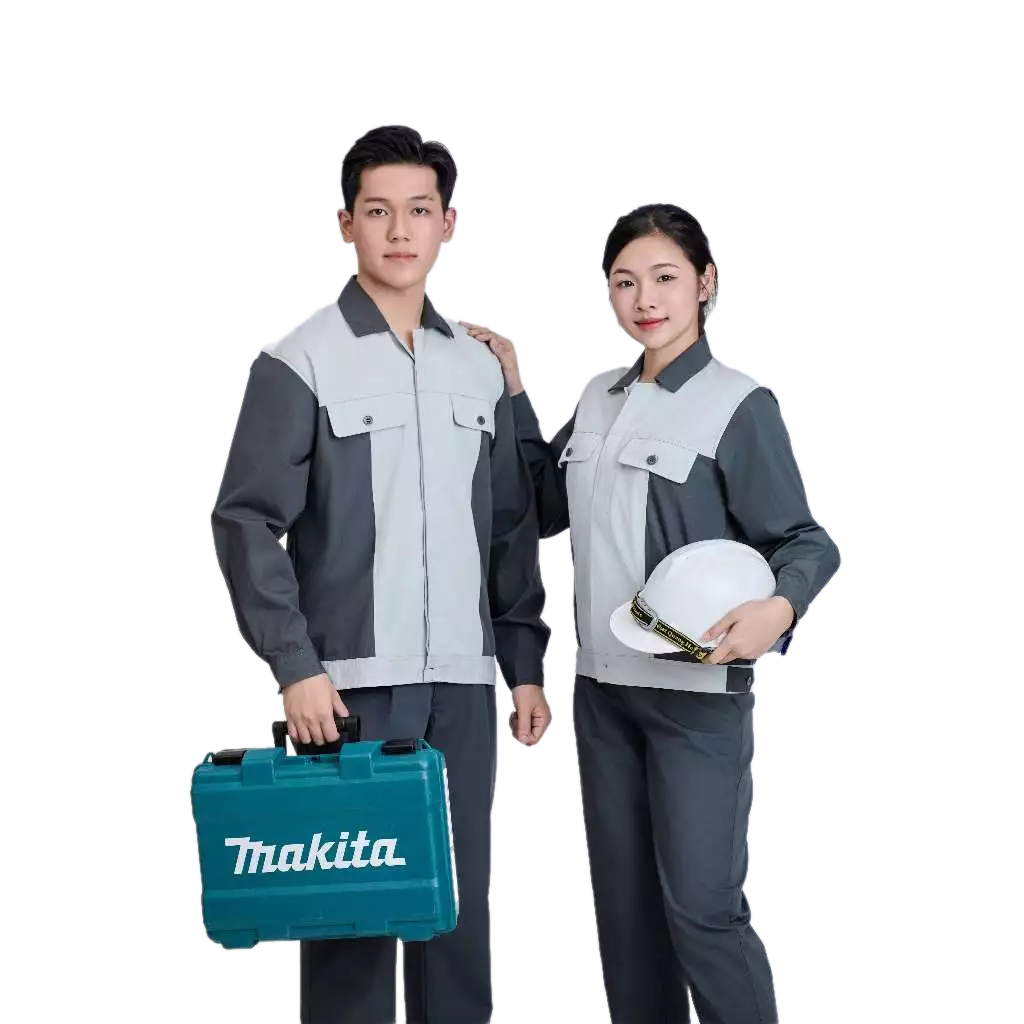

2. By Material
- Khaki fabric: Durable, breathable, and dust-resistant.
- Polyester-cotton blend: Easy to wash, quick-drying, and wrinkle-resistant.
- Chemical-resistant materials: PVC plastic and synthetic rubber offer maximum protection from chemicals.
- Heat-resistant fabrics: Asbestos, ceramic fiber, and fireproof materials provide protection in high-temperature environments.
- Waterproof fabrics: Suitable for wet environments with high water resistance.
Criteria for Choosing High-Quality Protective Clothing
- Meets safety standards: Choose products that comply with ISO and national safety standards.
- Material suitability: Select materials based on workplace hazards such as heat, chemicals, or physical impact.
- Comfortable design: Clothing should allow free movement and be breathable.
- Durability and easy maintenance: Ensures long-term use and cost-effectiveness.
- Industry-appropriate color: Some industries require specific colors for better identification.
- Additional protective accessories: Such as helmets, gloves, and masks for comprehensive protection.
How to Maintain Protective Clothings
- Proper washing: Use suitable detergents and avoid harsh chemicals to maintain fabric quality.
- Dry in a well-ventilated area: Avoid direct sunlight to preserve fabric durability.
- Regular inspections: Check for damages and replace or repair clothing as needed.
- Correct storage: Keep in a dry, clean space to prevent mold and deterioration.
- Immediate cleaning after use: Especially for chemical-resistant and fireproof clothing to ensure continued protection.
Important Notes When Using Protective Clothing
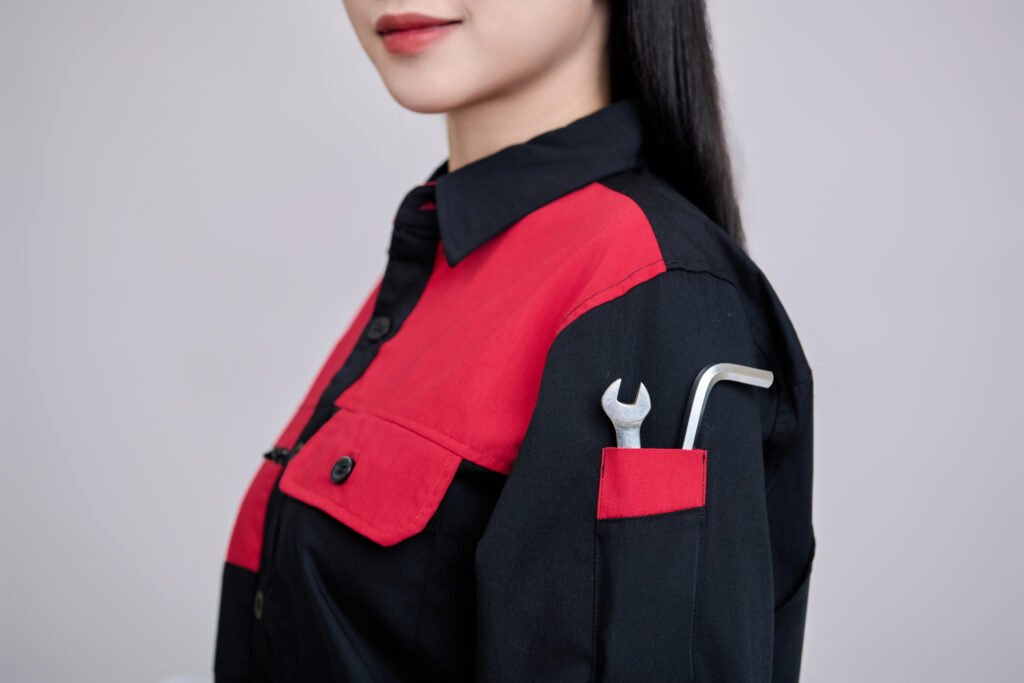

- Wear it correctly: Ensure all parts are properly secured for maximum safety.
- Use with other protective gear: Such as safety glasses and boots for complete protection.
- Avoid using damaged clothing: If clothing shows signs of wear, replace it immediately.
- Choose the right size: Overly loose or tight clothing can hinder movement and efficiency.
Conclusion
Protective clothing is an essential tool for workplace safety. Selecting the right type based on job hazards not only protects workers but also enhances productivity. Businesses and individuals should invest in proper protective gear and maintenance to maximize its benefits.
Using protective clothing is not just a regulatory requirement but also a commitment to workers’ health and safety. High-quality protective gear minimizes risks and fosters a more professional and efficient work environment.





 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt

Sản phẩm
Red And Black Short-Sleeve Workwear Set
Red And Black Long-Sleeve Workwear Set
Blue And Grey Short-sleeve workwear set
BLUE+GREY LONG-SLEEVED WORKSUIT
CHARCOAL+GREY SHORT-SLEEVED WORKWEAR
CHARCOAL+GREY LONG-SLEEVED WORKWEAR
SHORT-SLEEVED REFLECTIVE GRAY WORKSUIT
LONG-SLEEVED REFLECTIVE GRAY WORKSUIT
GREY COORDINATE LONG-SLEEVED NAVY
NAVY POLO JERSEY
POLO BLUE+NAVY JERSEYS FOR MEN AND WOMEN
POLO JERSEY NAVY+WHITE MEN’S/WOMEN’S